What is electronic invoice
Electronic invoicing refers to the digital exchange of accounting documents between buyers and sellers. E-invoice is not always limited to the invoice itself but can mean a family of structured fiscal documents exchanged electronically, such as credit notes, debit notes, purchase orders, waybills, and more. Generally, transaction data is submitted to the tax authority for validation before being forwarded to the recipient. These documents are typically formatted as XML or JSON files, containing all necessary details. In most cases, PDF files can’t be accepted as a valid electronic invoice format.
B2B E-invoice mandates – obligation to issue E-invoies between businesses – are currently in place in various countries globally including Turkey, Italy, Argentina and Mexico, which are the pioneers of the regulation. Other countries like France, Germany, Poland and Greece are in the process of establishing this obligation by applying for deregulation from EU law which asks for buyer’s consent to receive electronic invoices in digital format, usually as the first step of the mandate. After that, they make B2B E-invoicing mandatory. In addition, B2G electronic invoicing is already mandated across the EU under Directive 2014/55/EU, which requires public administrations to accept structured invoices.
To ensure interoperability across Europe, the European standard EN 16931 defines the core elements of an E-invoice. Additionally, formats such as Peppol BIS are widely used to create a standard way of exchanging electronic invoices across borders, enabling businesses and governments to follow common electronic invoice standards.
What is electronic invoice benefits
Every business that sells goods and provides services, whether subject to tax or not, can benefit from electronic invoice processing. Large enterprises usually prefer to adopt electronic invoicing solutions from service providers. This motivation comes from the large number of invoices they issue from their ERP accounting software. The time-wise efficiency and cost advantages of electronic invoice management reflect on their choices to switch to an E-invoicing platform. Also, in recent years, it can be seen that small and medium enterprises are increasingly issuing electronic invoices either within their accounting software or externally by a service provider.
Electronic invoice benefits include reduced paperwork, faster approval workflows, easier invoice processing, and improved compliance with E-invoice requirements. Beyond efficiency, digital invoicing reduces the risk of fraud and human error, while improving data accuracy for audits and reporting.
Another important benefit is environmental sustainability. By replacing paper invoices with E-invoicing solutions, companies contribute to lower paper consumption, reduced transportation needs, and decreased carbon emissions, which is increasingly valued by stakeholders and regulators.
How does E-invoicing work?
The electronic invoice submission process can be summarized in three main steps:
- Businesses extract the relevant invoice data from their accounting system.
- The electronic invoicing software document is created by the supplier before submission to the tax authority.
- Once the tax authority assesses and validates the E-documents according to the standards, it either transmits them directly to the recipient in electronic or PDF form, or sends them back to the supplier which should send them to the recipient.
Who is eligible for E-invoice?
Every business that sells goods and provides services, whether subject to tax or not, can decide to move forward with electronic invoicing system adoption. Large enterprises usually prefer to adopt E-invoice software because of their high transaction volumes. Small and medium enterprises may choose to issue electronic invoices either within their accounting software or externally by a service provider.
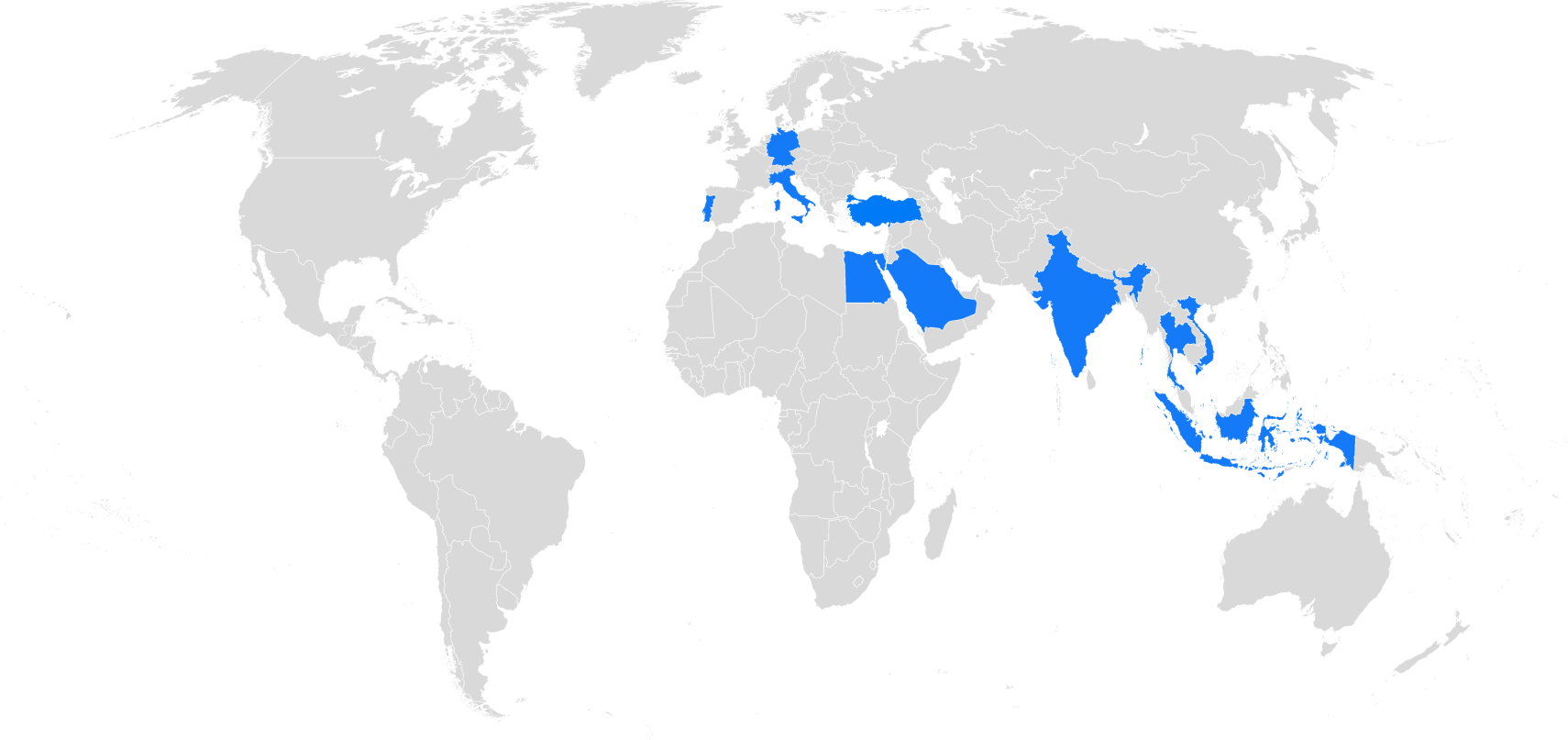
E-invoicing Countries
Currently, E-invoicing mandates are already in force or officially announced in several countries across the globe, including but not limited to Italy, Turkey, Mexico, Brazil, Chile, Argentina, Peru, Colombia, Uruguay, South Korea, Taiwan, Saudi Arabia, and Egypt.
In addition, many countries are in the process of transition, with phased rollouts or upcoming deadlines, here are some examples:
- India (10 crore+ turnover, ongoing)
- Indonesia (2026–2028)
- Portugal (2025–2026)
- Germany (2025–2028)
- France (2026–2027)
- Poland (2026)
- Greece (2025–2026)
Electronic invoicing is mandatory between taxpayers in several jurisdictions, but scope, timeline, and submission details differ depending on the country. In most cases, non-compliance with E-invoice requirements can lead to penalties, fines, or the rejection of invoices by tax authorities, which makes compliance a critical part of digital transformation strategies.
Future Outlook
As governments around the world continue to digitize tax processes, the role of electronic invoicing systems and software adoption will grow further. The European Commission’s VAT in the Digital Age (ViDA) initiative and the OECD’s framework for continuous transaction controls highlight the importance of a harmonized approach. Businesses that prepare early for these changes by investing in E-invoicing platforms and ensuring proper E-invoice integration will be better positioned to remain compliant and competitive in the evolving global market.
SNI’s Solution
SNI’s solution streamlines this workflow. SNI E-invoice integration automatically extracts the relevant invoice data and formats them as electronic XML (or JSON) files in any ERP system. Users can monitor the whole progress using SNI’s electronic invoice portal. Via the SNI Connector, the E-documents are submitted to the tax authority for E-invoice validation. If successfully validated, the invoice is forwarded to the counterparty. For incoming files from suppliers, SNI is able to receive the documents for the preferred ERP system at the incoming E-invoicing Cockpit.
Modern electronic invoicing software integration allows connectivity with various ERP systems (such as SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, or NetSuite), accounting platforms, and even e-commerce tools. This ensures that companies of all sizes can embed E-invoicing solutions into their existing IT infrastructure without replacing core systems.
How does SNI differentiate itself from other e-invoicing providers in the market?
SNI differentiates itself through its SAP-native integration, which eliminates the need for external middleware and allows businesses to manage e-invoicing directly in their ERP environment. Unlike many providers that rely on standalone platforms, SNI offers a user-friendly cockpit for both outbound and inbound invoices, ensuring full visibility and traceability. In addition, SNI’s coverage spans 40+ countries, enabling clients to manage multiple jurisdictions through a single solution. With ongoing regulatory monitoring, proactive updates, and direct communication with tax authorities, SNI ensures compliance while simplifying operations and reducing IT complexity.
What invoice format compatibility and conversion capabilities does SNI offer?
SNI supports a wide range of invoice standards and syntaxes, including XML, JSON, UBL, CII, Peppol BIS, and country-specific schemas. The solution can automatically convert invoices between structured formats and human-readable outputs such as PDF/A-3. This means businesses can issue invoices in one format and have them validated or delivered in another, depending on regulatory requirements. Additionally, SNI’s system includes a mapping engine that adapts ERP data to multiple formats, ensuring compliance with local standards. With this capability, businesses avoid costly format incompatibility issues and ensure smooth communication across diverse e-invoicing ecosystems.
How does SNI support multi-country e-invoicing operations for global businesses?
SNI is designed for multinational organizations that need to comply with different tax authorities, schemas, and submission models worldwide. Through a centralized cockpit, companies can manage all invoices, regardless of jurisdiction, in one place. The solution covers clearance models, post-audit models, and B2G platforms across more than 40 countries. SNI continuously monitors global regulatory changes and delivers timely updates to its clients. This reduces the burden of managing separate providers for each market and ensures consistent compliance. Businesses gain efficiency, visibility, and simplified audit readiness across all their global invoicing operations.
What implementation and compliance support services does SNI provide to clients?
SNI offers end-to-end implementation support, including data mapping, process analysis, and ERP integration. The project owners work closely with clients to configure workflows in line with both business needs and legal obligations. Beyond initial deployment, SNI provides continuous compliance updates ensuring that changes in legislation or technical schemas are reflected in the system without disruption. Clients also benefit from a dedicated support manager throughout their operations.
What security protocols does SNI use to protect invoice data and transactions?
SNI applies industry-leading data protection and cybersecurity standards to safeguard sensitive financial information. All invoice transmissions use encrypted communication channels (HTTPS, TLS), and stored data is protected with AES encryption. Access to the system is controlled through role-based authorization, audit logs, and user authentication mechanisms. For clients operating in highly regulated industries, SNI offers compliance with GDPR and ISO 27001 standards. In addition, data exchanges with tax authorities follow secure API protocols. These measures ensure that invoice data remains confidential, tamper-proof, and compliant with both international and local data security regulations.
Does SNI handle both B2B and B2G e-invoicing transactions?
Yes. SNI’s solution is built to cover both B2B and B2G e-invoicing requirements. For B2B, invoices are exchanged directly between businesses or via clearance platforms depending on local legislation. For B2G, SNI connects to official government portals and ensures invoices are formatted and submitted according to public sector requirements. By supporting both transaction types in a single cockpit, SNI allows companies to comply seamlessly with a wide range of obligations while avoiding duplication of systems or processes.
How does e-invoicing prevent invoice fraud?
E-invoicing reduces fraud by ensuring that invoices are validated by tax authorities or platforms before reaching recipients. Structured formats (XML, JSON) prevent unauthorized alteration of key data such as VAT, totals, or transaction dates. Mandatory validation and clearance models make it much harder for fake invoices to circulate, since each document carries a unique identifier and digital signature. Additionally, audit trails and secure submission channels provide traceability for every transaction. By integrating these controls directly into ERP systems, e-invoicing eliminates the manual handling risks that often lead to duplicate, inflated, or fictitious invoices in paper-based environments.
How do I assess if SNI meets my business's specific e-invoicing requirements?
To assess fit, businesses should begin with a compliance and requirements mapping exercise. This involves reviewing local obligations in each operating country, identifying ERP integration needs, and evaluating reporting and archiving requirements. SNI provides detailed solution demos, technical documentation, and country coverage lists, which allow companies to compare features with their compliance roadmap. Businesses can also request a proof of concept to validate performance in their own environment. By aligning SNI’s capabilities with their invoicing volumes, formats, and geographic footprint, organizations can determine whether the solution meets both present and future e-invoicing demands.


